Getting Started¶
Here, you will be briefly guided through the basics of how to use strym. Once you are set, the following tutorials go straight into analysis of CAN data file, driving data identification, characterization and many more.
Strym data is capable of handling timeseries data obtained from Comma.ai Panda and Giraffe Connector.
Most functions and methods in strym expects timeseries data of following format
The main entry point of strym is strymread class.
Most functions and methods in strym expects timeseries data of following format
Time |
Message |
|
1 |
1582056042.5040324 |
2.0 |
2 |
1582056043.5040324 |
2.1 |
3 |
1582056044.5040324 |
2.12 |
4 |
1582056045.5040324 |
1.98 |
5 |
1582056046.5040324 |
1.6 |
Here, data should be of type Pandas.DataFrame with two columns: Time and Message.
However, scope of strym is not limited to timeseries data obtained from comma.ai Panda.
Any timeseries data of above format is capable of harnessing methods available in strym.
strym workflow at a glance¶
Import strymread:
import strym
from strym import strymread
Read your data¶
Read your data file (.csv) using:
dbcfile = 'newToyotacode.dbc'
r =strymread(csvfile="2020-08-15/2020-08-15-08-29-45_2T3Y1RFV8KC014025_CAN_Messages.csv", dbcfile=dbcfile)
However, you may not need to provide dbc file as strymread infers dbc file from the name of the CSV file. We recommend, the name of CSV file include VIN number. By default, if vin number is not found, then strymread defaults to selecting DBC file for Toyota RAV4.
The object r stores data from CSV file in one of its attributes
dataframe.
Message Retrieval and Visualization¶
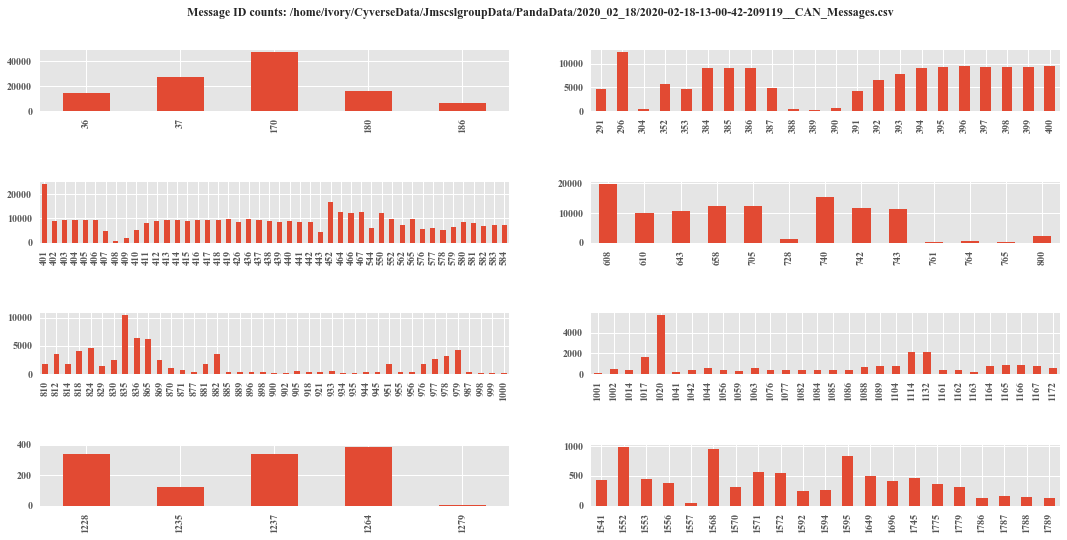
Before you proceed to do anything, always get counts of Messages. The count method returns a dataframe with counts of message grouped by separate BUS ID.
Get the count data:
count = r.count(plot = True)
count
Output:
MessageID |
Counts_Bus_0 |
Counts_Bus_1 |
Counts_Bus_2 |
TotalCount |
36 |
31626 |
0 |
31626 |
63252 |
37 |
63252 |
0 |
63252 |
126504 |
⋮ |
⋮ |
⋮ |
⋮ |
⋮ |
2025 |
17 |
0 |
17 |
34 |
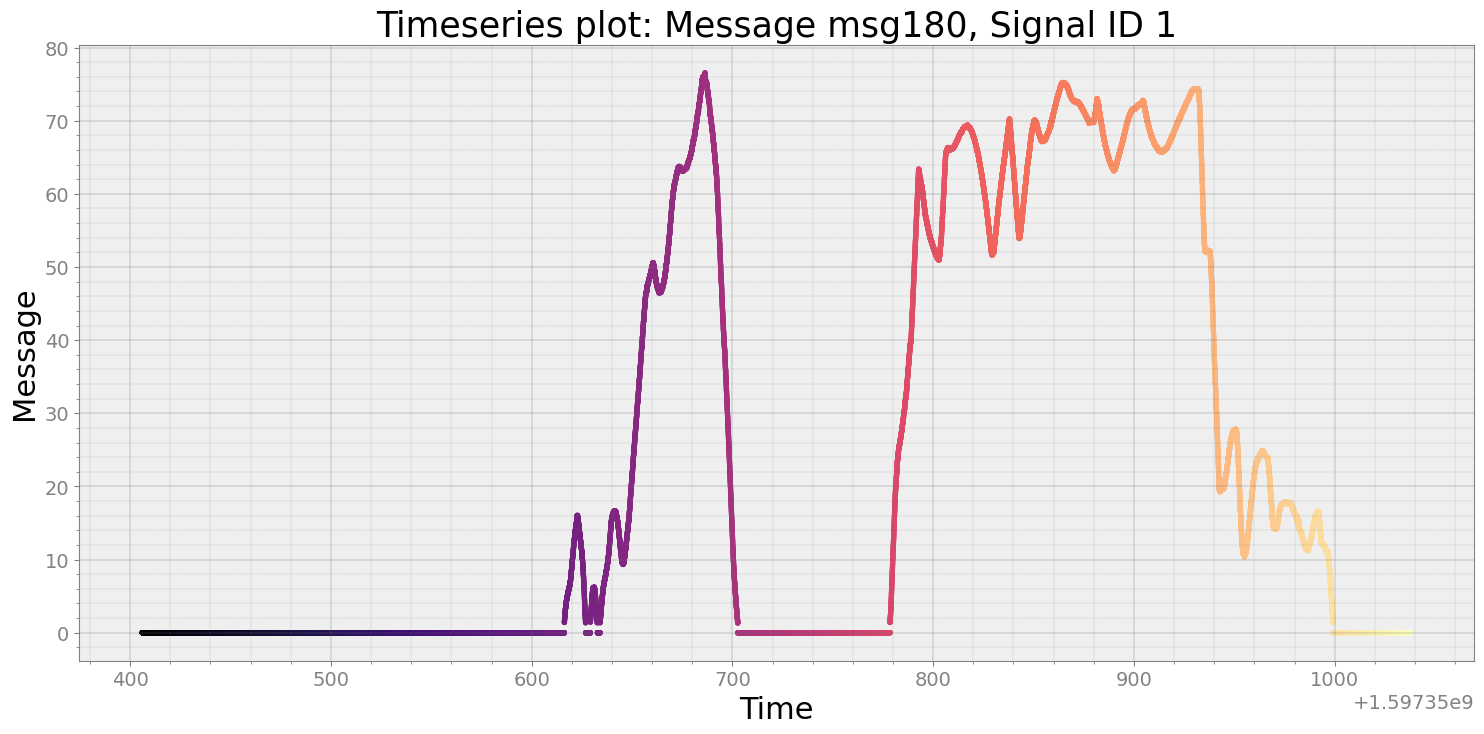
Reading a signal from a particular message ID¶
strymread allows the retrive timeseries data from a specific signal of a particular message ID:
msg180 = r.get_ts(msg=180, signal=1)
strymread.plt_ts(msg180, title="Message msg180, Signal ID 1")
Quality Check of Data Rate of Particular Message¶
strymread provides methods for quality checking of data rate of signal/message ID:
ts_speed = r.speed()
strymread.ranalyze(msg180)
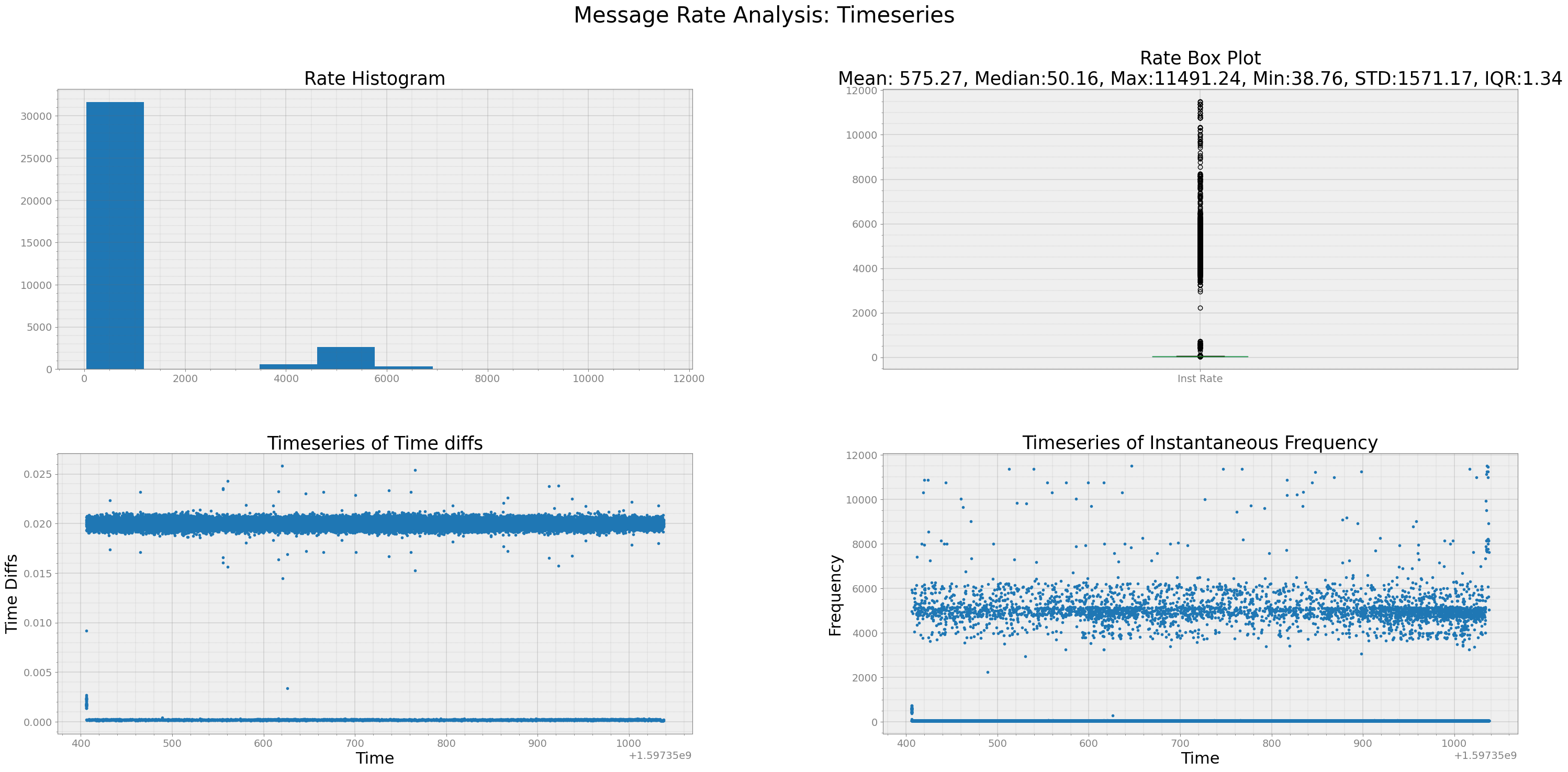
From above plots, we can see that message 180 are received at the rate of 50 Hz approximately, but ocassionaly messages have also come in burst. In such case, care needs to be taken while doing further analysis of messages specifically when we do temporal analysis.